LIMITED EDITION:
Pumpkin Spice
and Salted Caramel
Find Your Favorite




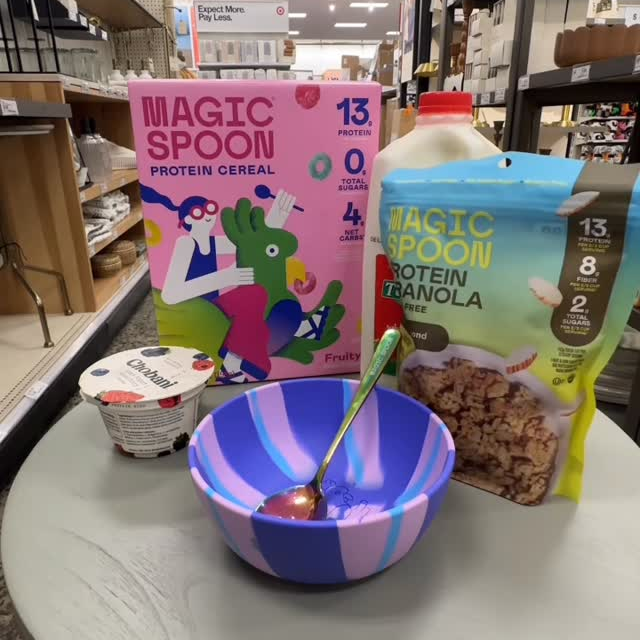
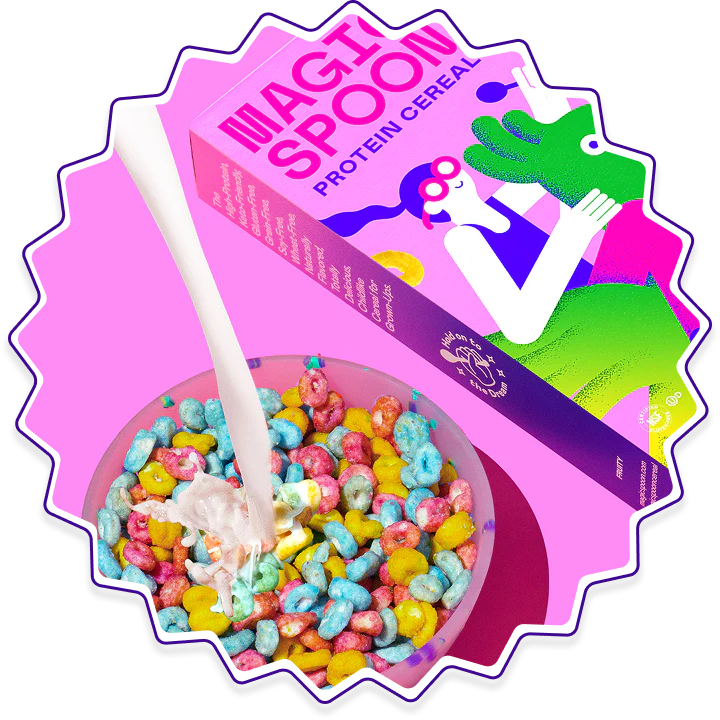
Cereal

Cereal

Cereal

Treats

Get your childhood favorites delivered
to your door monthly
Subscribe & Save 20%
Free bowl set with your first order
VIP Access to limited-edition launches
Change flavors anytime
Skip or cancel delivery anytime

Shop Best Sellers


High Protein
12g-14g complete protein in every bowl.

0-2g Sugar
No cane sugar, corn syrup, or sugar alcohol.

Sweet & Delicious
Tastes just like you remember, only better.
“With cereal that tastes
this good and offers so much … Magic Spoon may be the future of breakfast.”

“There’s a new magician in the kitchen.”
“Magic Spoon has become my new go-to for one simple reason: it’s delicious.”

I just ate delicious cereal for
dinner and the last time I did
that was my sophomore year in
college!
dinner and the last time I did
that was my sophomore year in
college!
KELLY LEVEQUE
KELLY LEVEQUE
Holistic Nutritionist, Wellness Expert,
and Celebrity Health Coach
and Celebrity Health Coach

When they said ‘Breakfast of Champions’, they meant Magic Spoon.
Priscilla Frederick-Loomis
Priscilla Frederick-Loomis
Olympian, Entrepreneur, Radio Personality, Podcast Host & Public Speaker

Magic Spoon is my adult life and kid life smashed into one fantastic box of cereal.
Natalie Duran
Natalie Duran
Rock Climber, Ninja Warrior, Neuroscientist, Producer

Why did we grow
up, but our cereal didn't?